Diagnosis
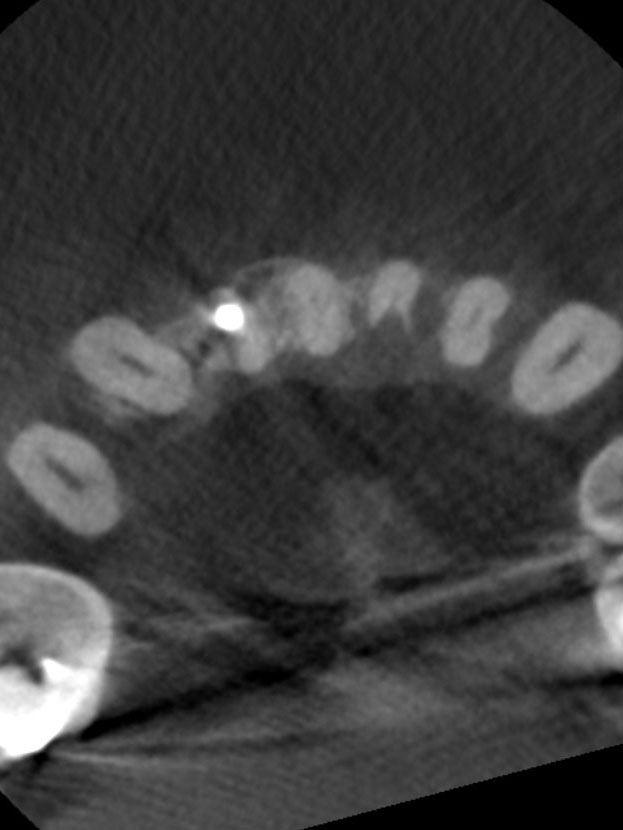
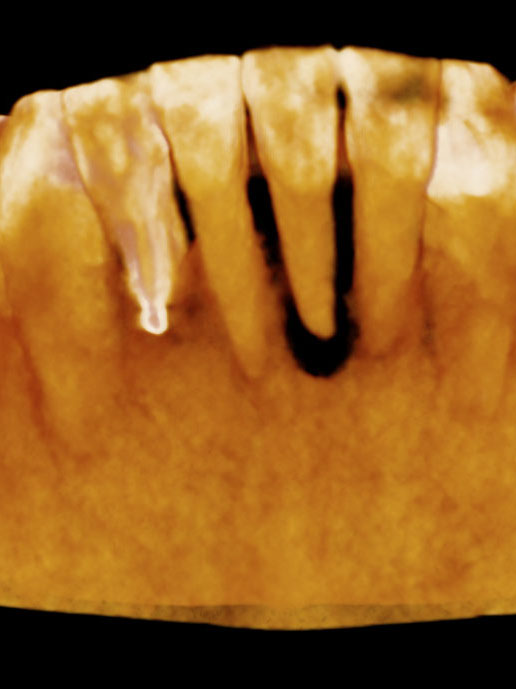
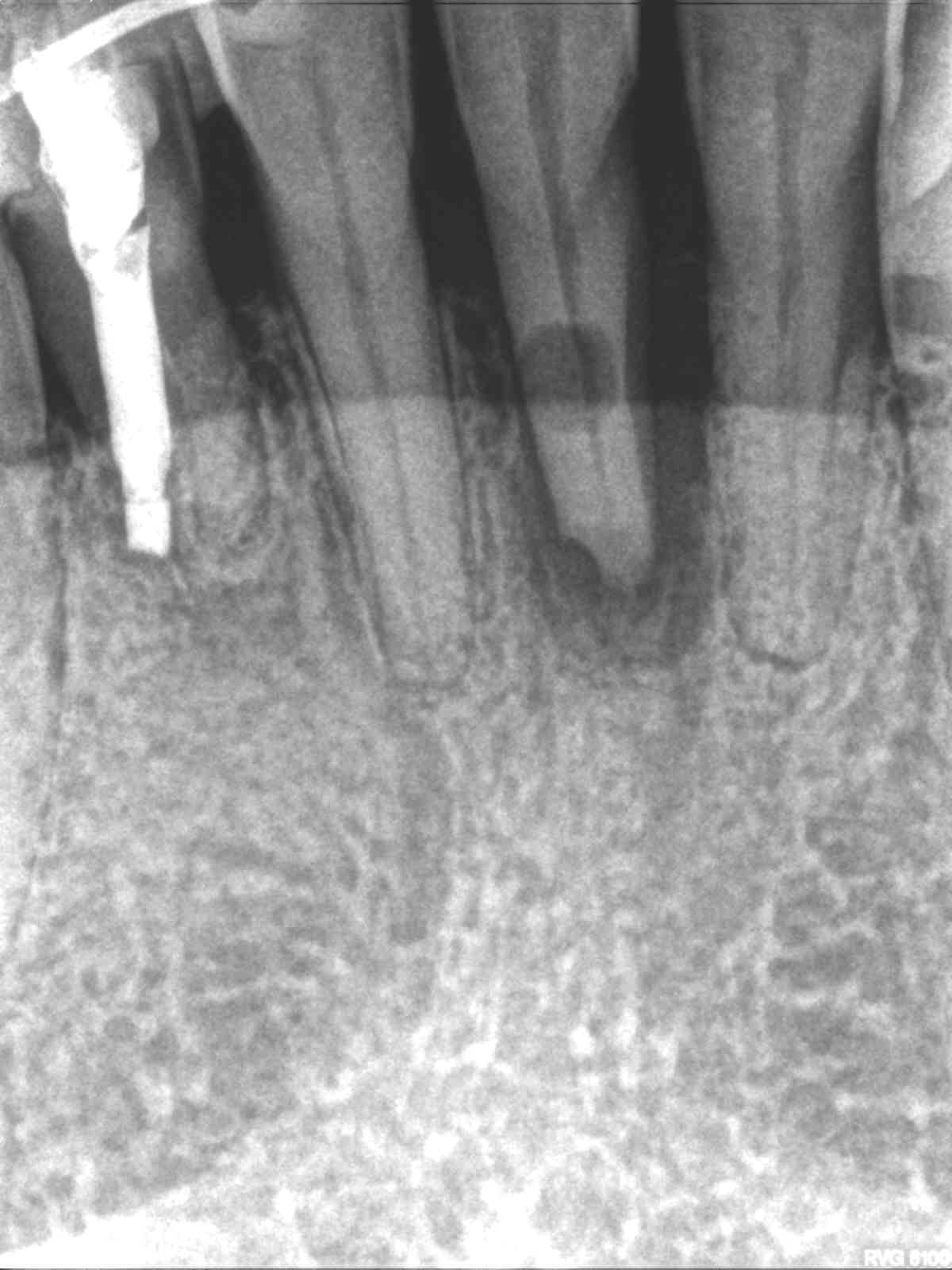
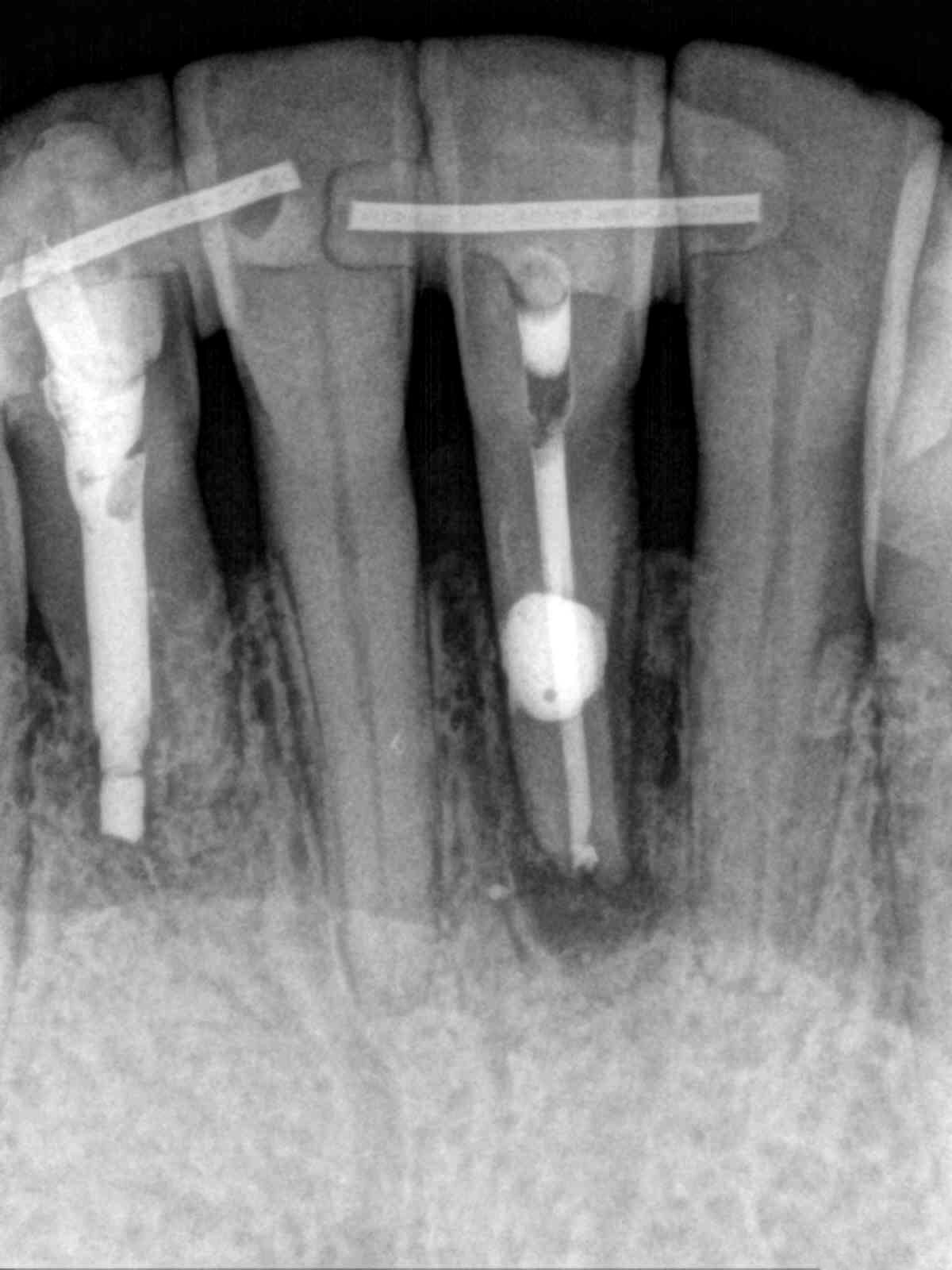
Patient presented the chief complaint of a loose lower front tooth. Clinical examination revealed a non-restored tooth #24 with class 3 mobility and tenderness to percussion and palpation. Radiographs revealed a mid-root radiolucency communicating with the apex and bone loss extending up the mesial root surface to the crestal bone. CBCT displayed external inflammatory resorption on the lingual of tooth that communicated with the pulp. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of pulpal necrosis with symptomatic apical periodontitis and external resorption.
Challenge
The extensive bone loss and excessive clinical mobility made the prognosis for treatment very poor. In addition, the location of the external resorptive defect (on the lingual of tooth #24) magnified the difficulty of this case.
Treatment
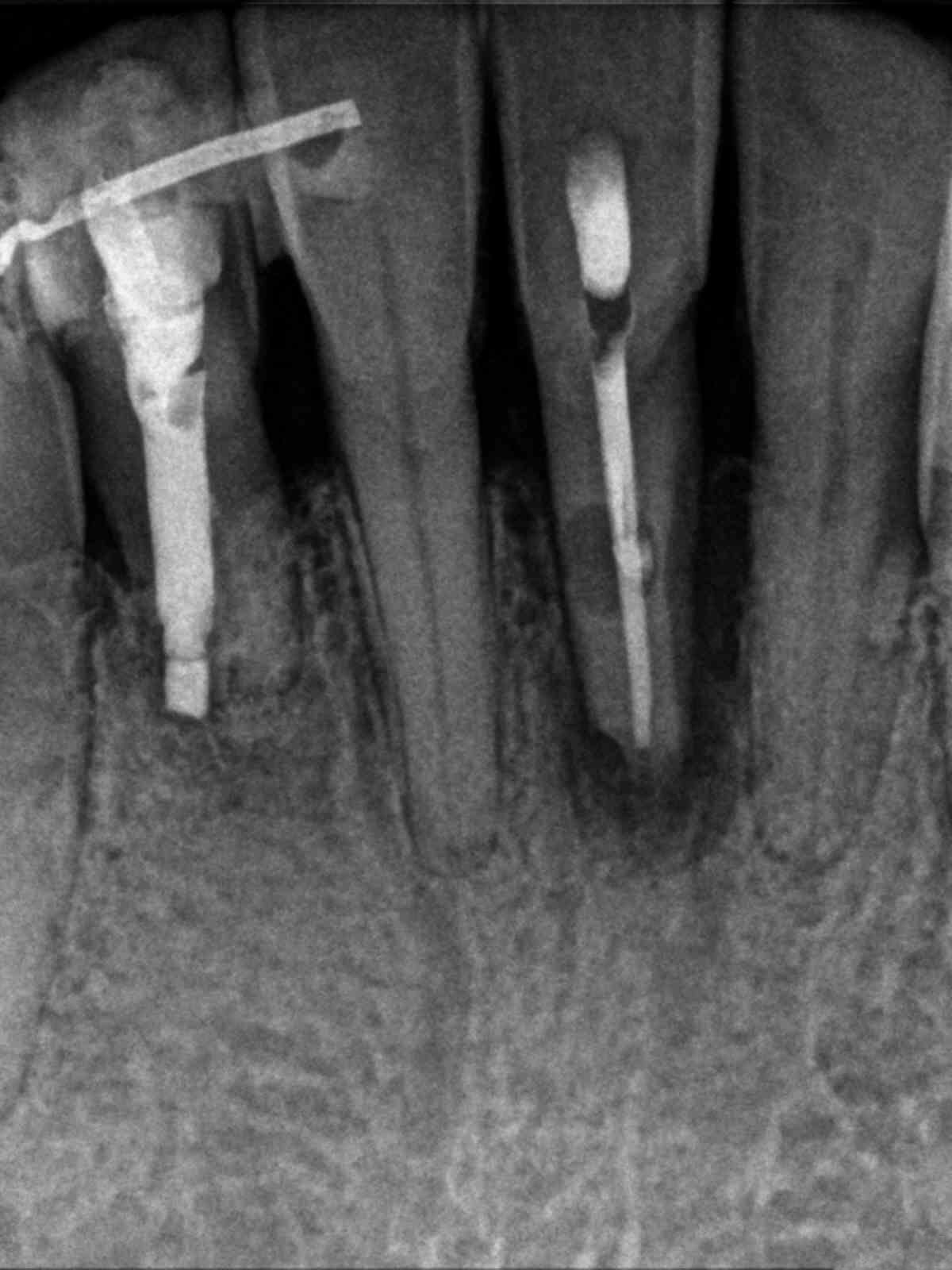
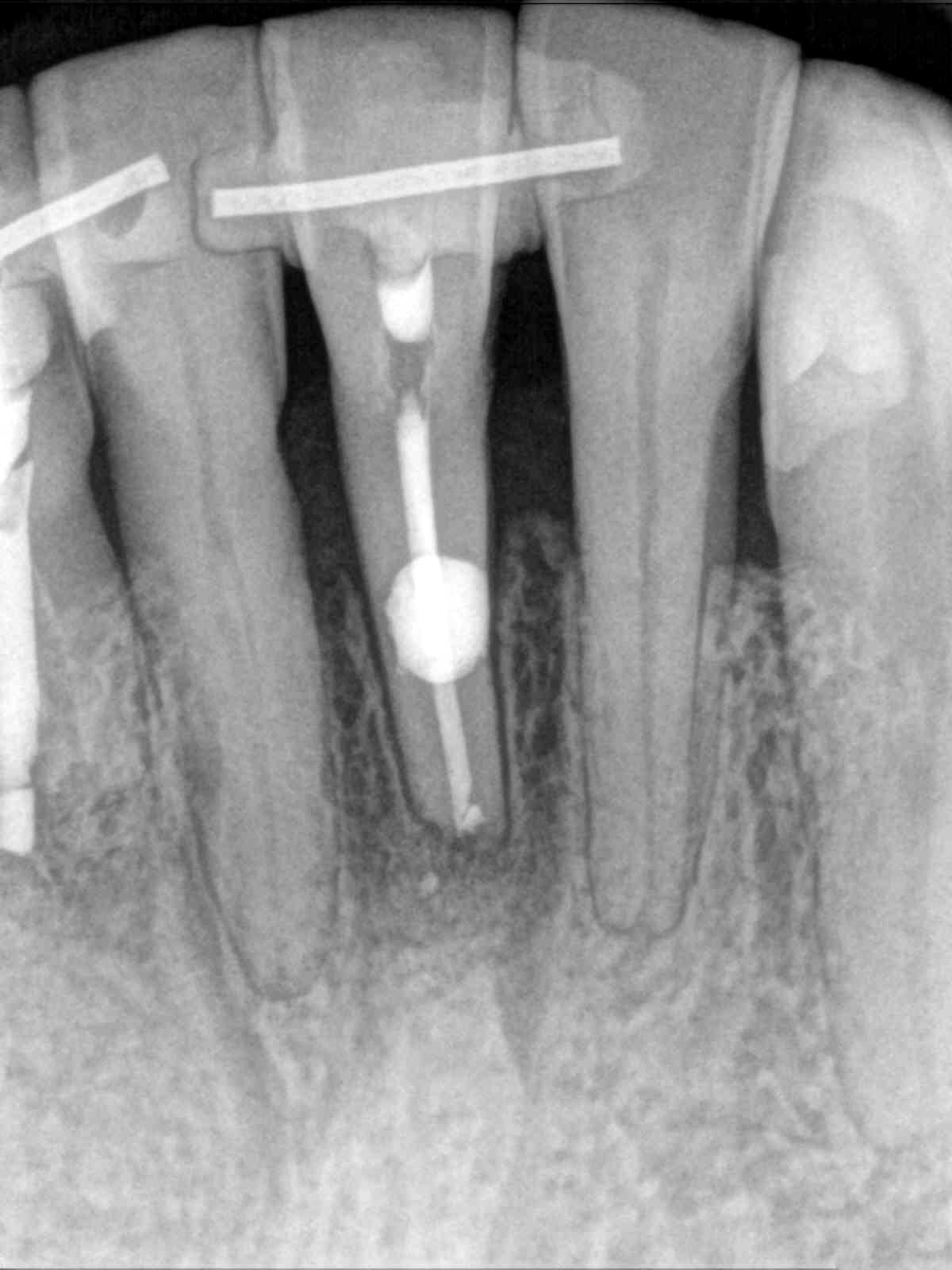
Root canal treatment was completed over two visits, medicating with calcium hydroxide. A lingual splint was placed by the patient’s general dentist to stabilize the tooth. Surgical repair of the lingual resorptive defect treatment with Geristore, apical surgery with a bioceramic putty retrofilling, scaling and root planning were also performed. 6-month recall shows resolution of the radiolucency with bone fill up to the crestal bone.