Diagnosis
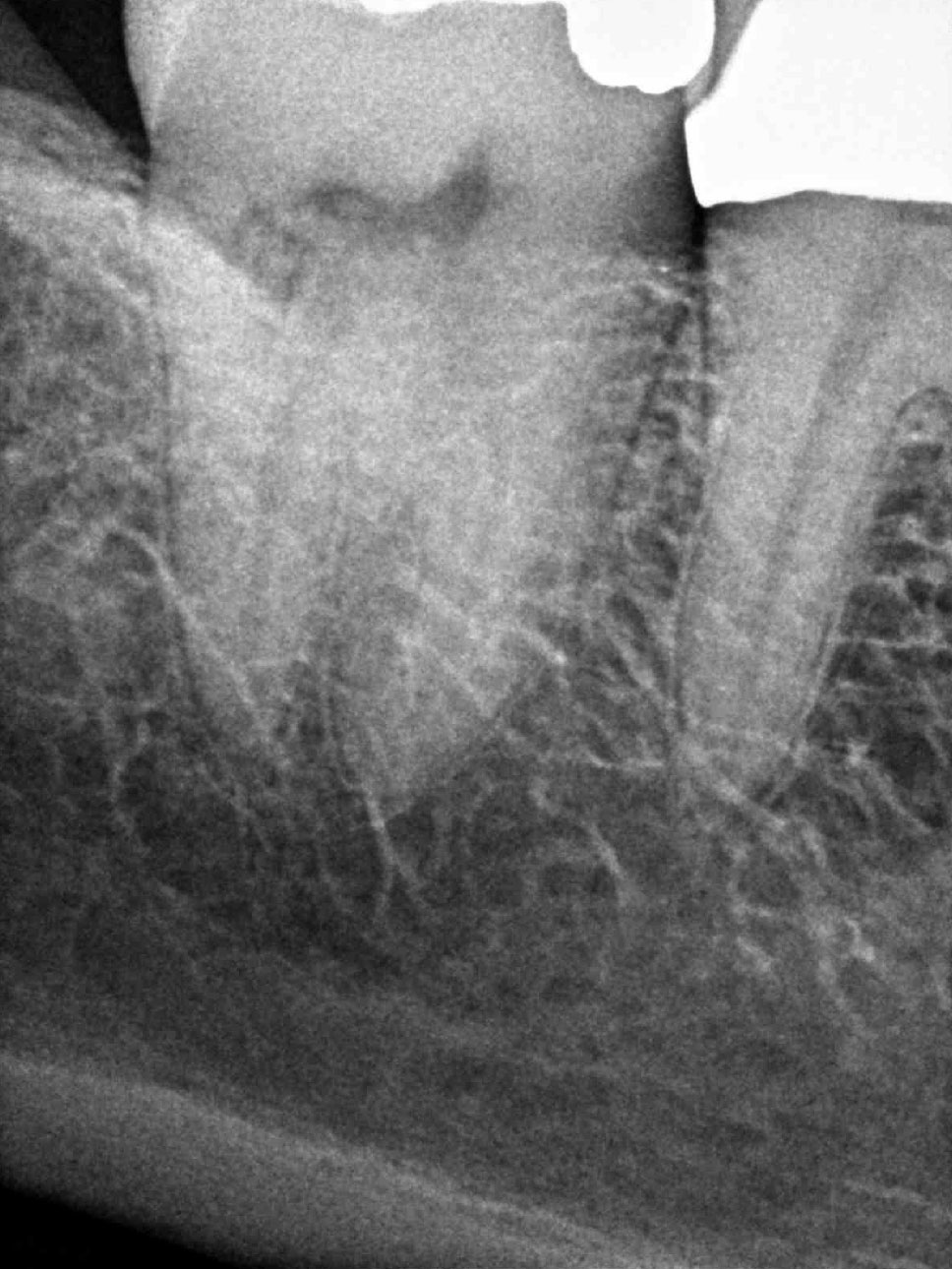
Patient is asymptomatic; but, aware that tooth #31 has had a resorptive defect for over ten years. There is no evidence of the defect upon visual inspection and clinical findings are within normal limits.
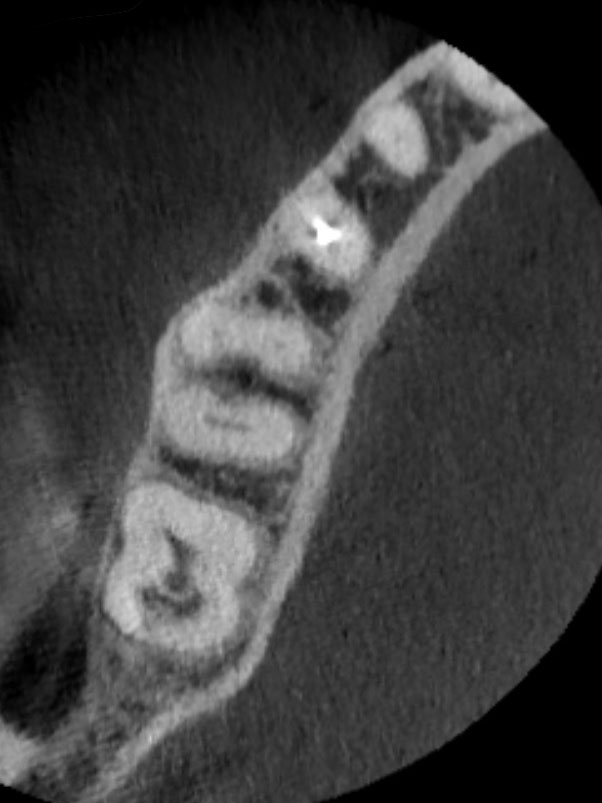
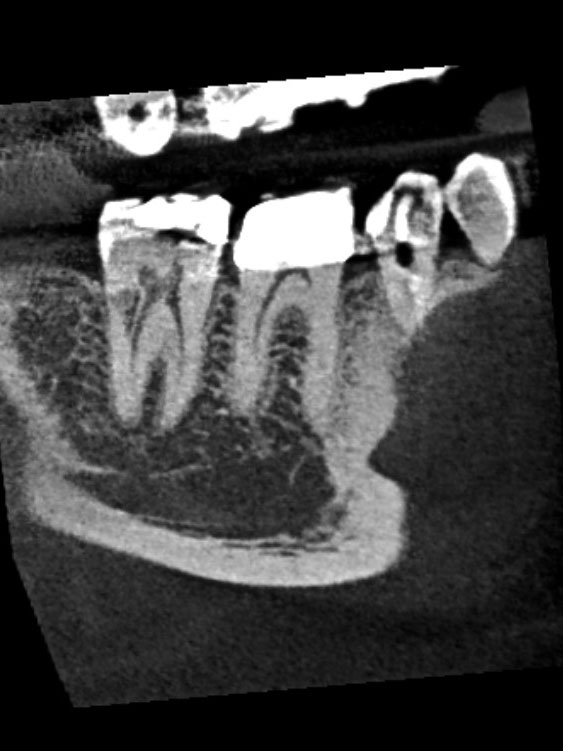
CBCT images display a resorptive defect on the distal aspect involving the dentin and communicating with the periodontal ligament. This defect extends into the middle third of the root; but, does not communicate with the pulp chamber or distal canal. These findings support a diagnosis of normal pulpal and periapical tissues, with an external resorptive defect.
Challenge
It is often difficult to ascertain if the resorptive process is active or arrested. Comparing the current radiograph with those taken several years in the past can assist in this evaluation and help determine the most optimal treatment plan.
Treatment
The lesion has been present and unchanged on radiographs (10+ years). Patient opted to re-evaluate in 6 months with a repeat CBCT. If the lesion increases in size, treatment options would be considered at that time.